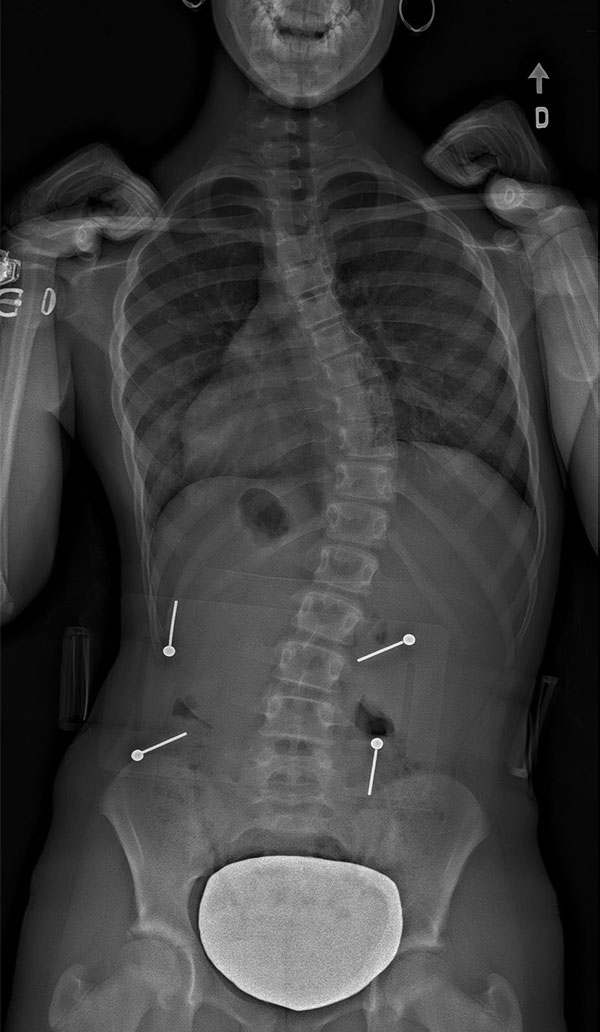
WHAT IS SCOLIOSIS?
Scoliosis is a 3D deformation of the spine involving torsion which translates into a lateral curvature of over 10° as well as abnormal rotation of the vertebrae. Often described as an S-shaped deformation, a scoliotic spine more accurately resembles a spiral staircase.
Thoracic scoliosis (dorsal) – same level as the ribcage.
![Scoliosis [image]](../img/photo_scoliose_01a.jpg) |
 |
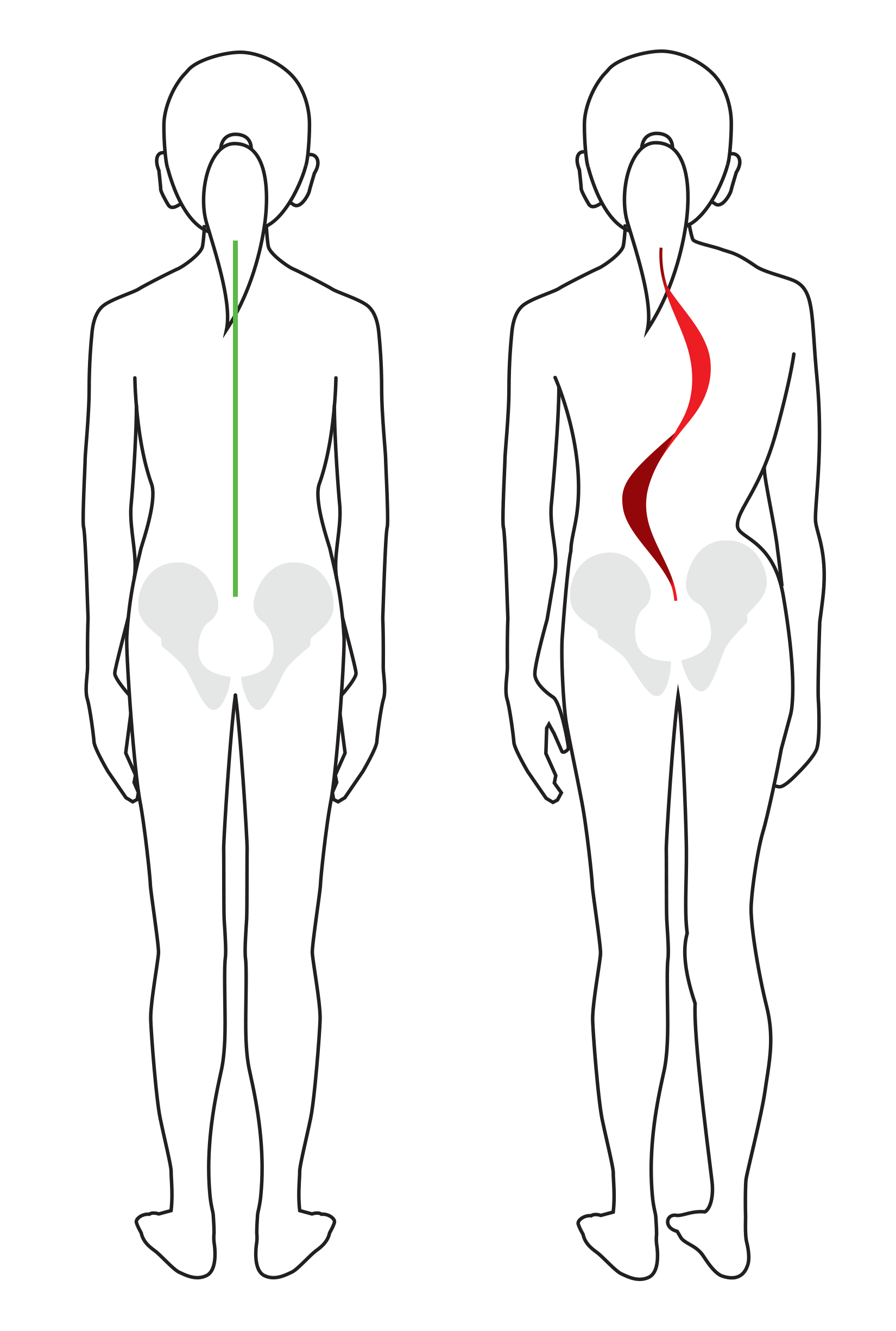
CONSEQUENCES OF SCOLIOSIS
While the majority of cases of scoliosis are mild and require only that curve progression be monitored, scoliosis in its advanced form goes beyond a 3D deformation of the spine and is a pathology that affects the entire musculoskeletal system.
In fact, advanced cases of scoliosis can lead to the destabilization of the entire spine which in turn affects overall posture.
This postural disorganization then goes on to cause neuro-musculoskeletal disorders. The latter, be they directly or indirectly related to scoliosis, eventually come to further its progression.
![Scoliosis [image]](../img/photo_scoliose_06_en.png)
Some examples of scoliosis-related neuro-musculoskeletal disorders:
- backaches, neck pain
- sciatica
- osteoarthritis
- herniated disc
- cauda equina syndrome (spinal stenosis)
- incontinence
- migraines
- intervertebral instability (spondylolisthesis, laterolisthesis, anterolisthesis, retrolisthesis)
- vertebral subluxation
- rotatory subluxation
- radiculopathy
- thoracic insufficiency syndrome (compression of vital organs such as the heart and lungs)
As scoliosis can eventually lead to such various disorders, a preventive treatment like SpineCor®, which simultaneously addresses the neurological, muscular and skeletal aspects of the affliction can clearly be of benefit to the patient. It is also possible to combine scoliosis-specific exercises and chiropractic Remodeling care to potentiate the brace’s effect.
![Scoliosis [image]](../img/photo_scoliose_01b.jpg)
As the child bends forward, the prominence on their back becomes noticeable, indicating the presence of a scoliosis.


